What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the development of computer systems that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
You may also be interested in Natural Language Processing as well.
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence
Here's why Artificial Intelligence is helpful:
- Gets Things Done Faster
- Helps Make Better Choices
- Makes Work Easier
- Opens Doors to New Ideas
Doing Things Faster and Easier
Artificial Intelligence (AI) helps get things done faster and easier in many industries. It makes tasks smoother, saves time, and lets people work on more important things.
Making Smarter Choices
AI helps us make better decisions by analyzing lots of data quickly. Whether it's predicting trends or personalizing services, AI gives us insights to make smart choices.
Making Work Less Stressful
AI takes care of repetitive tasks so people can focus on more interesting jobs. This makes work less tiring and more enjoyable.
Finding New Ideas
AI discovers new ideas by finding patterns in large amounts of data. This leads to fresh discoveries and innovations across different fields.
In summary, the main benefits of Artificial Intelligence are its ability to expedite tasks, improve decision-making, simplify work processes, and foster innovation. AI accelerates task completion, enhances decision-making through data analysis, streamlines workflows, and encourages innovative discoveries by identifying patterns in data.
Downsides of Artificial Intelligence
Let's talk about the bad sides of Artificial Intelligence:
- It can make people lose jobs and worsen money differences.
- It might be unfair and treat people differently.
- It can be bad for privacy and safety.
- We might rely too much on AI and use it in wrong ways.
Ethical Concerns: Job Loss and Money Differences
Artificial Intelligence can make some people lose their jobs and make the gap between rich and poor bigger. Jobs that people used to do might now be done by machines, which can make it hard for people to find work and make money. Also, not everyone might get the good things that come from AI, so money differences could get worse.
Risks of Unfairness and Discrimination
AI might not treat everyone the same way and might make unfair choices. It learns from old information, which could be unfair, so it might keep making unfair choices. This can be really bad in things like picking who gets a job, giving loans, and enforcing laws, and it can hurt people and groups unfairly.
Privacy and Safety Worries with AI
Using a lot of Artificial Intelligence can bring up big worries about privacy and safety. AI often needs lots of personal information to work well, which can make it easy for others to know too much about us without us wanting them to. Also, AI can have mistakes or be used by bad people to hurt others or take their personal info.
Overreliance on AI and Wrong Use
Depending too much on AI can be risky. If we rely too heavily on AI to make important choices, it could be a big problem if it doesn't work right or if someone uses it the wrong way. Also, using AI too much might mean we forget how to do things ourselves, which could make us weak.
In short, The main downsides of Artificial Intelligence are making people lose jobs and making money differences worse, being unfair and treating people differently, raising privacy and safety worries, and making us rely too much on it and use it wrong.
History of Artificial Intelligence
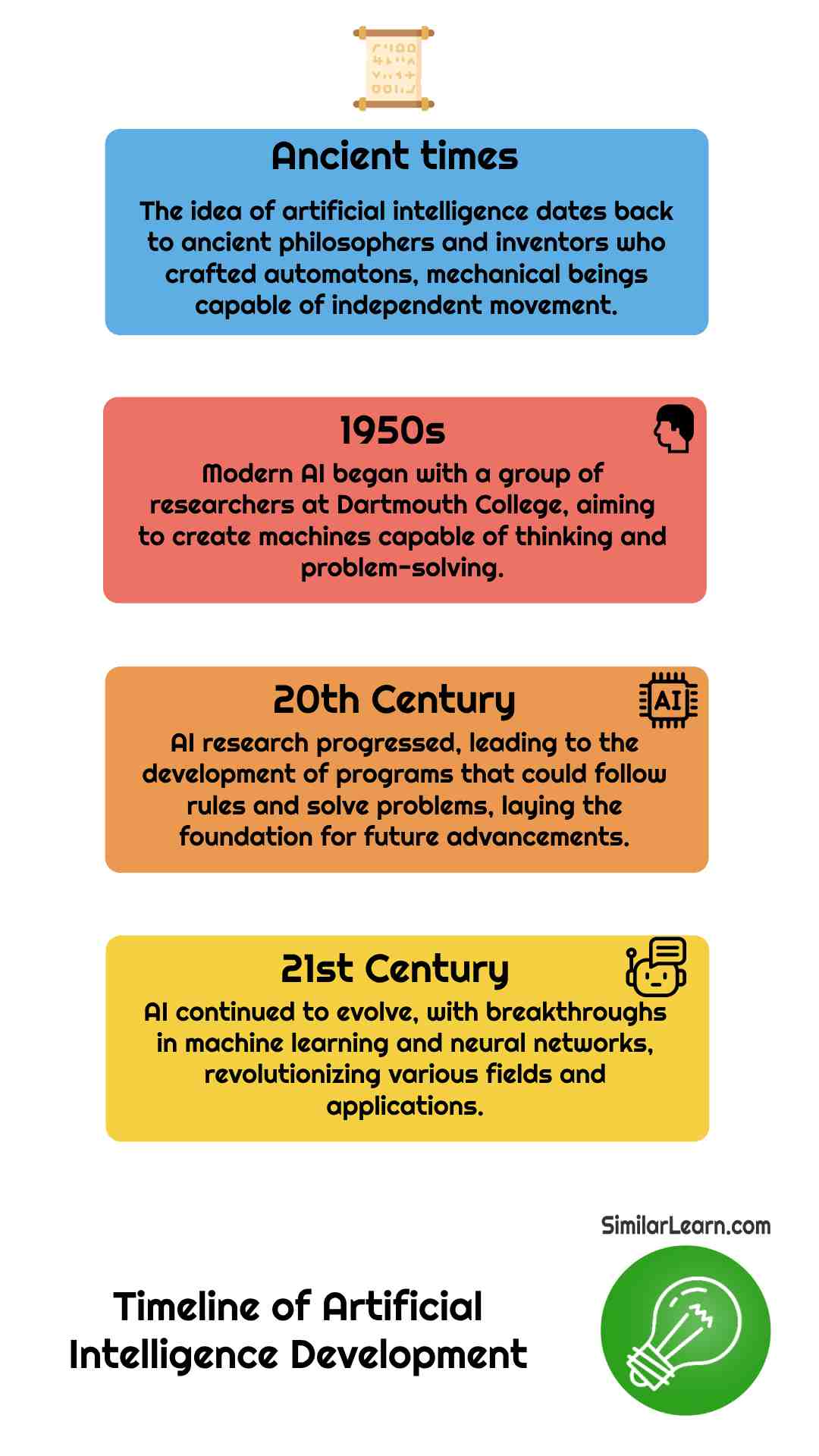
Origins and Early Days
The concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been around for thousands of years, back to ancient times when people were already thinking about creating intelligent beings. Ancient philosophers pondered questions about life and death, imagining beings that could think and act like humans.
In those ancient times, inventors created what they called "automatons." These were like early robots as mechanical creations that could move on their own, without needing someone to control them. These automatons fascinated people, showing that it was possible to make something artificial that could mimic life in some way.
Big Steps Forward
Fast forward to the 20th century, and AI started to become a serious field of study. In the 1950s, a group of researchers gathered at Dartmouth College and said, "Let's make machines that can think!" This was the beginning of modern AI. They started by making programs that could follow rules and solve problems – like figuring out math puzzles or finding the best move in a game.
Getting Smarter Over Time
As time passed, AI got even smarter. Instead of just following instructions, machines began to learn from experience. Scientists created something called neural networks, which are like computer brains. These neural networks helped machines get really good at things like recognizing faces in photos or understanding what people are saying.
How History Shaped AI
Throughout history, events have influenced the development of AI. Sometimes, there was a lot of excitement and funding for AI research, and progress happened quickly. Other times, people got worried about what AI could do and slowed things down. But no matter what, AI kept moving forward, thanks to smarter technology and people working together.
In summary, AI history stretches over millennia, starting with ancient thinkers and progressing to modern technology; the Dartmouth Conference in the 20th century kickstarted contemporary AI, and over time, rule-based systems transformed into neural networks, allowing machines to learn, despite hurdles, collaborative efforts and technological breakthroughs continue to drive AI advancement across various fields.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Here are fifteen types of artificial intelligence:
- Reactive machines
- Self-aware
- Theory of mind
- Artificial general intelligence
- Super AI
- Artificial superintelligence
- Theory of mind AI
- Natural language processing
- Robotics
- Expert system
- Reinforcement Learning
- Chatbots
- Smart assistants
- Narrow AI
- AI alignment
You may also be interested in Natural Language Processing as well.
Reactive machines
Reactive machines are AI systems that react to their environment based on pre-programmed rules.
An example of a reactive machine is a thermostat that adjusts the temperature based on predefined settings in response to changes in room temperature.
Check also our Free AI Detector page.
Self-aware
Self-aware AI systems are those that possess consciousness or an understanding of their own existence.
While true self-aware AI doesn't exist yet, some researchers are working on developing self-monitoring and self-improving algorithms that could be considered early steps toward self-awareness.
Theory of mind
Theory of mind AI is capable of understanding and attributing mental states, such as beliefs, intentions, and desires, to themselves and others.
An example of this could be AI systems used in customer service that analyze customer behavior and tailor responses based on inferred emotions or needs.
Artificial general intelligence (AGI)
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is AI that can understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks, similar to humans.
While AGI doesn't currently exist, it is the ultimate goal of many AI researchers and could potentially revolutionize numerous industries and fields once achieved.
Super AI
Super AI surpasses human intelligence across all domains and tasks.
One example of a super AI system is AlphaGo, an AI developed by DeepMind that defeated world champion Go players.
AlphaGo's ability to analyze and strategize in the complex game of Go demonstrated a level of intelligence beyond human capabilities in that specific domain.
Artificial superintelligence (ASI)
Artificial superintelligence (ASI) is AI that possesses intelligence far superior to that of humans.
While ASI remains theoretical, experts often speculate on the potential implications of achieving such advanced AI, including its impact on society, economics, and even existential threats.
Theory of mind AI
Theory of mind AI is capable of understanding and responding to human emotions, beliefs, and intentions.
An example of this is Emotion AI technology developed by companies like Affectiva, which uses facial recognition and other biometric data to infer human emotions and tailor responses or interactions accordingly.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and interpret human language.
One notable example of NLP in action is Google's Smart Reply feature, which suggests responses to emails based on the context and content of the message.
Robotics
Robotics involves the design and creation of physical machines that can perform tasks autonomously or under human supervision.
An example of robotics in AI is Boston Dynamics' Spot robot, which is capable of dynamic locomotion and manipulation tasks, such as carrying payloads or navigating complex environments.
Expert systems
Expert systems are AI systems that emulate the decision-making abilities of human experts in specific domains.
One example of an expert system is IBM's Watson, which is used in various fields, including healthcare and finance, to analyze data and provide insights and recommendations comparable to those of human experts.
Reinforcement learning
Reinforcement learning is a machine learning paradigm where agents learn to make decisions by interacting with an environment.
An example of reinforcement learning in practice is DeepMind's AlphaGo, which learned to play the game of Go by playing against itself and improving its strategy through trial and error.
Chatbots
Chatbots are AI-powered conversational agents designed to simulate human-like conversation.
An example of chatbot usage is the customer service chatbots employed by companies like Bank of America, which assist customers with account inquiries, transaction history, and other banking-related tasks through natural language interactions.
Smart assistants
Smart assistants are AI-based software programs designed to perform various tasks and provide assistance to users.
A popular example of a smart assistant is Amazon's Alexa, which can answer questions, control smart home devices, play music, and perform a wide range of other tasks through voice commands.
Check also our Free AI Detector page.
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, is designed for specific tasks or problems.
One example of narrow AI is Tesla's Autopilot system, which uses computer vision and deep learning algorithms to assist with driving tasks such as lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and automatic lane changes.
AI alignment
AI alignment is the process of ensuring that AI systems are aligned with human values and goals.
One example of AI alignment efforts is the development of ethical guidelines and principles for AI research and deployment, such as the Asilomar AI Principles and the AI Ethics Guidelines published by organizations like the IEEE and the European Commission.
Conclusion
In summary, AI brings both good and bad things. We need to use it carefully and make sure we follow rules to avoid problems. If we balance making new things with being careful, AI can help us without causing harm.
FAQ
Can you explain artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and mimic human actions, such as problem-solving, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and learning from experience.
How is AI used today?
AI is used in various industries and applications, including healthcare (for diagnosis and personalized treatment), finance (for fraud detection and algorithmic trading), customer service (through chatbots and virtual assistants), transportation (for autonomous vehicles), and many others.
What are 4 types of artificial intelligence?
The four types of artificial intelligence are reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind, and self-aware AI; reactive machines operate based on predefined rules and do not have memory, limited memory AI can learn from historical data, theory of mind AI is hypothetical, possessing human-like cognitive abilities such as understanding emotions and intentions, and self-aware AI would have consciousness and understanding of its own existence.
Who created AI?
The concept of artificial intelligence has evolved over time with contributions from various researchers and scientists, including Alan Turing, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others.
How did AI begin?
The idea of artificial intelligence dates back to ancient times, but modern AI research began in the 1950s; the term "artificial intelligence" was coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference, where researchers gathered to discuss the potential of creating machines with human-like intelligence.
Who made the first successful AI?
There isn't a definitive answer to who made the first successful AI, as AI development has been a collaborative effort involving many researchers and breakthroughs over decades.
Who is the father of AI?
There is no single "father of AI," but some prominent figures in the field include Alan Turing, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Herbert Simon, among others.
Who created ChatGPT?
ChatGPT was created by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research laboratory, and is based on the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture developed by OpenAI's research team.
Does Elon own OpenAI?
Elon Musk was one of the co-founders of OpenAI and has been involved with the organization, but he does not own it outright.
Does AI have privacy?
AI itself does not have privacy as it is a technology, but concerns arise regarding the privacy of individuals' data that AI systems may process or analyze.
Is AI actually a risk?
AI poses both opportunities and risks, as it has the potential to bring about significant advancements in various domains, but there are concerns about job displacement, algorithmic biases, and ethical implications.
Can AI take over your job?
AI has the potential to automate certain tasks and jobs, which may lead to job displacement in some industries, but it can also create new job opportunities and enhance productivity in others.
Does AI save money?
AI can lead to cost savings by automating repetitive tasks, improving efficiency, reducing errors, and optimizing resource allocation in various sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and customer service.
Is AI a good or bad idea?
The morality of AI depends on its application and how it is used; AI can be a force for good, driving innovation, improving productivity, and solving complex problems, but ethical considerations must be taken into account to mitigate potential negative consequences.
Is AI a good future?
AI has the potential to shape a better future by revolutionizing industries, enhancing human capabilities, and addressing global challenges, but responsible development and deployment of AI technologies are crucial to ensure positive outcomes.
What will AI do in 2050?
Predicting the exact capabilities and impact of AI in 2050 is speculative, but AI is expected to continue advancing and potentially playing significant roles in various aspects of society, from healthcare and education to transportation and entertainment.
Does Google have AI?
Yes, Google heavily invests in AI research and development and integrates AI technologies into many of its products and services, including Google Search, Google Assistant, and Google Photos.
Is Sophia the first AI?
Sophia is a humanoid robot developed by Hanson Robotics, but she is not the first AI; AI research and development have been ongoing for decades before Sophia's creation.
Can AI take over humans?
The idea of AI taking over humans, often portrayed in science fiction, is speculative and not supported by current scientific understanding; AI is a tool created and controlled by humans, and its capabilities are limited by its programming and design.
Can AI take over the world?
The notion of AI taking over the world is a common theme in fiction, but it is not a realistic concern based on current technology and understanding; AI systems are created and controlled by humans, and their actions are ultimately determined by human intentions and oversight.
Check also our Free AI Detector page.
